Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
5. It may take seconds up to a few minutes for Windows to
discover a DHCP server to
assign a private (LAN) IP address for a network adapter. Because
there is no DHCP server, then it automatically assigns itself a
private IP address from an APIPA address range. Automatic Private IP
Addressing (APIPA) is a feature that lets a Windows XP computer (and
several previous Windows versions namely Windows 98, 98 SE, ME, 2000,
Server 2003) assign itself an Internet Protocol (IP) address
when a DHCP server is not available. An APIPA IP address is a Class B IP address in this form 169.254.x.y where x and y are decimal numbers.
APIPA address range is from 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254 with a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
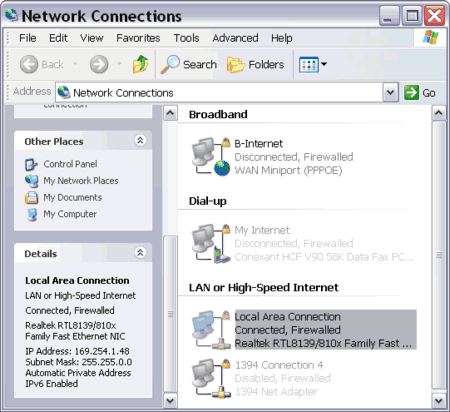
Figure:
Private IP address 169.254.x.y and subnet mask 255.255.0.0 on the first computer (PC-01)
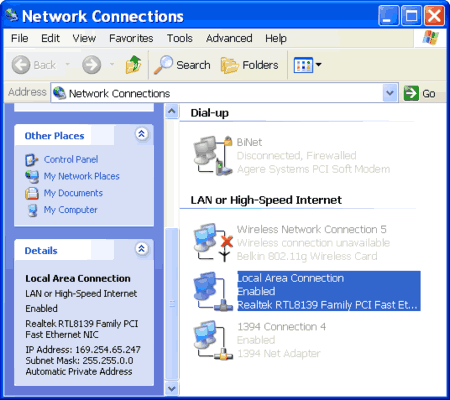
Figure:
Private IP address 169.254.x.y and subnet mask 255.255.0.0 on the second computer (PC-02)
|